Benzo withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, tremors, seizures, irritability, and increased sensitivity to stimuli. Benzodiazepine withdrawal occurs when someone who regularly uses medications like Xanax (alprazolam), Valium (diazepam), Ativan (lorazepam), or Klonopin (clonazepam) suddenly reduces or stops their intake. Due to their strong impact on the nervous system, benzodiazepine withdrawal can be severe and potentially life-threatening if not properly managed.
Understanding benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms is crucial for safe and effective detoxification and recovery.
Common Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal from benzodiazepines (benzos) commonly involves physical, psychological, and neurological symptoms. Here are the most frequently observed symptoms:
1. Anxiety and Panic Attacks
Heightened anxiety and recurring panic attacks are hallmark symptoms, often significantly worse than the original anxiety treated by benzodiazepines.
2. Insomnia and Sleep Disturbances
Insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns frequently occur during withdrawal as the central nervous system becomes overstimulated without benzodiazepines.
3. Tremors and Muscle Twitching
Physical tremors, shakiness, and muscle twitching often appear within hours or days after stopping benzodiazepines, reflecting neurological hyperactivity.
4. Sensory Hypersensitivity
Increased sensitivity to light, sound, touch, or smell often develops, making everyday environments feel overwhelming and uncomfortable.
5. Sweating and Chills
Excessive sweating, temperature fluctuations, and chills commonly occur as the body struggles to regulate itself without benzodiazepines.
6. Headaches and Dizziness
Frequent headaches, dizziness, and lightheadedness arise as neurological pathways adjust following benzodiazepine cessation.
7. Irritability and Mood Swings
Mood instability, irritability, and agitation typically emerge as the brain chemistry tries to rebalance itself after benzodiazepine discontinuation.
8. Cognitive Difficulties
Memory problems, confusion, and trouble concentrating are common, affecting everyday tasks and overall mental clarity.
Severe Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal from benzodiazepines can escalate into dangerous medical conditions, especially when the drugs are abruptly stopped:
1. Seizures
Withdrawal seizures represent one of the most severe risks associated with benzodiazepine discontinuation. These can occur within days of stopping the drug, especially following high-dose or long-term use.
2. Hallucinations and Delusions
Visual, auditory, or tactile hallucinations, as well as paranoid delusions, may develop during severe withdrawal, requiring immediate medical intervention.
3. Delirium
Severe confusion, disorientation, hallucinations, and agitation—collectively known as withdrawal delirium—can occur in extreme cases.
Timeline of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptoms
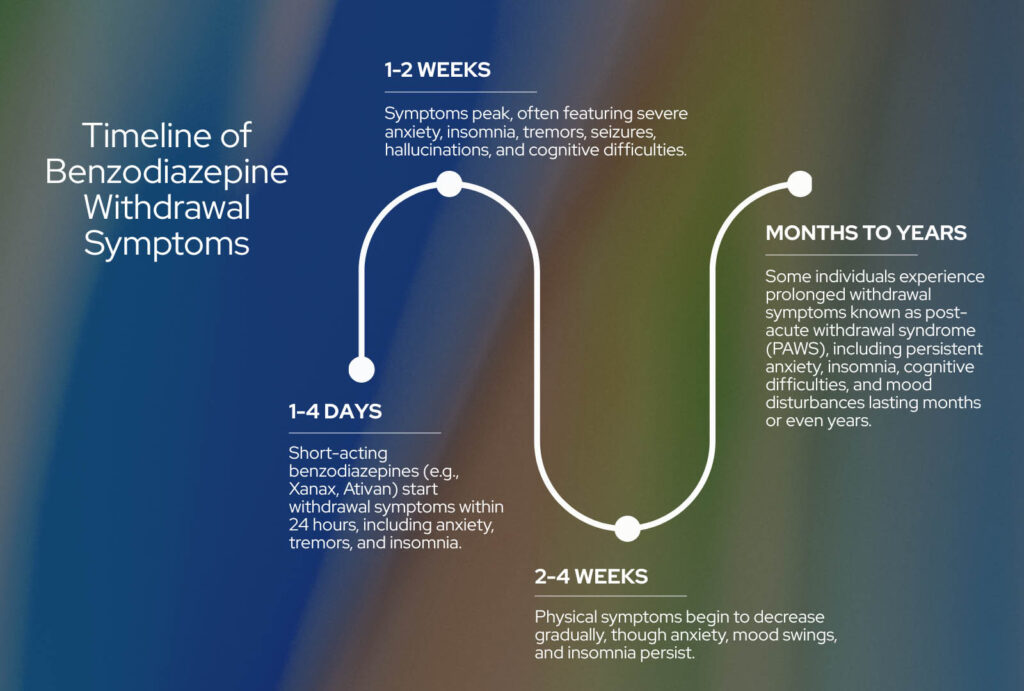
Benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms typically follow this timeline:
- 1–4 Days After Last Dose: Short-acting benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Ativan) start withdrawal symptoms within 24 hours, including anxiety, tremors, and insomnia.
- 1–2 Weeks After Last Dose: Symptoms peak, often featuring severe anxiety, insomnia, tremors, seizures, hallucinations, and cognitive difficulties.
- 2–4 Weeks After Last Dose: Physical symptoms begin to decrease gradually, though anxiety, mood swings, and insomnia persist.
- Months to Years (Protracted Withdrawal): Some individuals experience prolonged withdrawal symptoms known as post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS), including persistent anxiety, insomnia, cognitive difficulties, and mood disturbances lasting months or even years.
Factors Influencing Severity of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
Several factors significantly influence withdrawal severity:
- Length and Frequency of Use: Prolonged benzodiazepine use typically results in more severe withdrawal symptoms.
- Dosage: Higher benzodiazepine dosages increase withdrawal severity.
- Rate of Discontinuation: Sudden cessation intensifies withdrawal risks, while gradual tapering minimizes symptoms.
- Individual Health and Co-occurring Conditions: Existing mental health issues or physical conditions complicate withdrawal, increasing symptom severity.
How to Safely Manage Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptoms?

Due to potentially severe symptoms, benzodiazepine withdrawal requires careful management:
1. Gradual Medication Tapering
Slowly reducing benzodiazepine dosage under medical supervision is essential. Physicians often taper dosage gradually over weeks or months, reducing the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms.
2. Alternative Medications
Doctors may prescribe longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, to ease withdrawal symptoms and prevent seizures during detoxification.
3. Counseling and Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and counseling help manage anxiety, insomnia, cravings, and psychological withdrawal symptoms, improving recovery outcomes.
4. Lifestyle Management
Supporting overall health through adequate nutrition, hydration, sleep hygiene, exercise, and stress management helps reduce withdrawal severity and promotes long-term recovery.
Potential Complications of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
Withdrawal from benzodiazepines, particularly without medical supervision, can result in complications such as:
- Seizures and Neurological Damage: Severe withdrawal seizures can cause lasting neurological impairment or death.
- Mental Health Crises: Withdrawal can exacerbate existing anxiety or depression, leading to suicidal ideation or self-harm.
- Relapse and Dependence: Severe withdrawal symptoms significantly increase relapse risk, perpetuating benzodiazepine dependence.
When to Seek Medical Help for Benzodiazepine Withdrawal?
Immediate medical attention is essential if experiencing seizures, hallucinations, delirium, severe anxiety, suicidal thoughts, or uncontrollable withdrawal symptoms. Medical supervision dramatically reduces risks associated with withdrawal and supports safe recovery.
For comprehensive information and immediate help, consider our benzo addiction treatment program.
Understanding benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms and seeking proper medical guidance significantly enhance safety and long-term recovery success.






